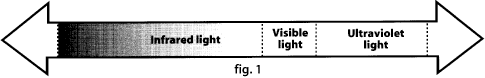
Interference Free Audio: The transmission
medium for infrared is a modulated carrier of harmless invisible
light ( Fig. 1) instead of Radio or Audio signals. It is immune
to outside interference and causes none itself. No operator licensing
is required for use of infrared systems.
Easy Installation: IR products are compact
and lightweight. Both transmitters and emitters feature a broad
range of mounting hardware options for simple, economical installation.
Unlike induction loop systems, no floor work or seating rearrangement
is necessary.
Flexibility: Infrared systems are offered
in both permanent installation and portable use, plus several
receiver models, some suitable for use with hearing aids.
No Interference: An infrared signal is contained
within the room in which it is used, so even adjacent rooms may
use identical infrared systems without interference among them.
Broad Coverage: Infrared light behaves much
like visible light.. With reflections from light-colored walls,
ceilings, and other surfaces, a receiver can see the signal without
a direct line-of-sight to the emitter. The receiver's ultra wide-angle
"Fish-Eye" lens captures direct or reflected signals from most
any direction (Fig 2.)
Universality: The same receivers can be used
in most courtrooms that use IR systems with the same frequencies.
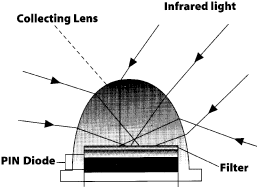
How It Works:
An Infrared system comprises three sections: The Transmitter,
the emitter (sometimes both combined in one unit), and the receiver.
The transmitter imparts the audio signal onto a subcarrier signal
which the emitter will convert into infrared light. The receiver
decodes the infrared signal to retrieve the original audio.
The critical elements of the Infrared link are the
optical components: The transmitting infrared light-emiiting diode
(IR-LED) and its counterpart, the IR light-sensitive receiving
diode. IR-LEDS are subjected to rigorous quality control inspection
and are carefully selected for maximum longevity. They will last
years longer than conventional IR-LEDS.
To achieve a usable radiated power level, The IR-LEDS
are used in multiple arrays. Their light output is amplitude modulated
by one or more frequency-modulated subcarriers (typically 2.3
MHz for single channel wide band systems and 2.3 MHz and 2.8 MHz
for two channel systems). Each Channel's Audio Signal Frequency-modulates
its particular subcarrier (Fig. 3.).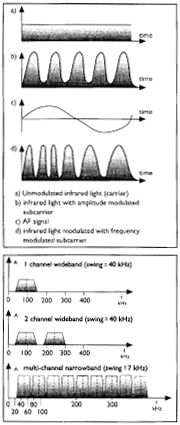
The receiving diodes are fitted with a collecting
lens and an integral filter which passes infrared light but attenuates
visible light to optimize sensitivity.
Two transmission modes are available: Wideband, for
one or two channels of high fidelity audio: or narrowband, for
up to 32 channels with a 50 to 8,000 Hz response suitable for
communications (fig. 4).
Multiple Room Usage
The advantages of infrared systems are fully realized in applications
where different audio programs are required in adjacent rooms,
such as Court Houses. Each room can be equipped with one SME IR
Court Room System without interference among them. No frequency
coordination is required as with radio frequency systems. The
same receiver can be used in any Court Room.
A facility utilizing infrared ensures the patron
that the installed infrared system meets the highest standards
of reliability and fidelity. There are thousands of facilities
with infrared systems in operation today.